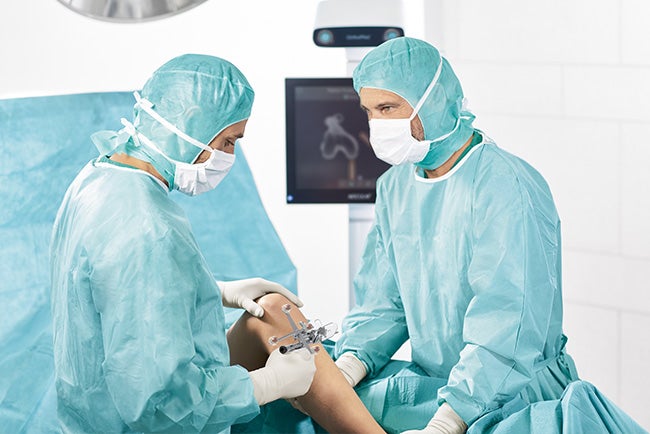
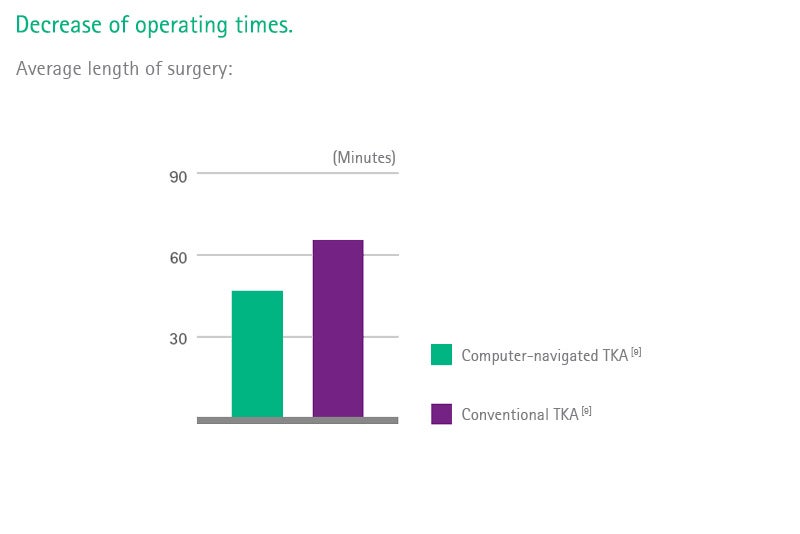
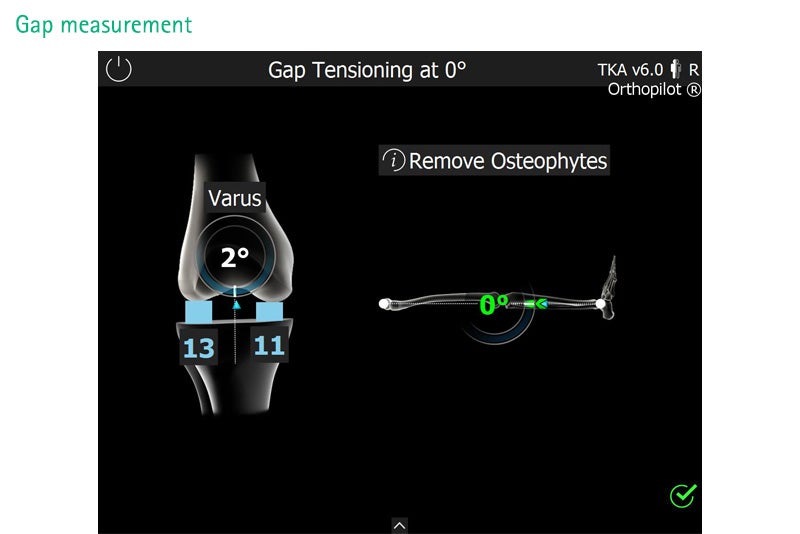
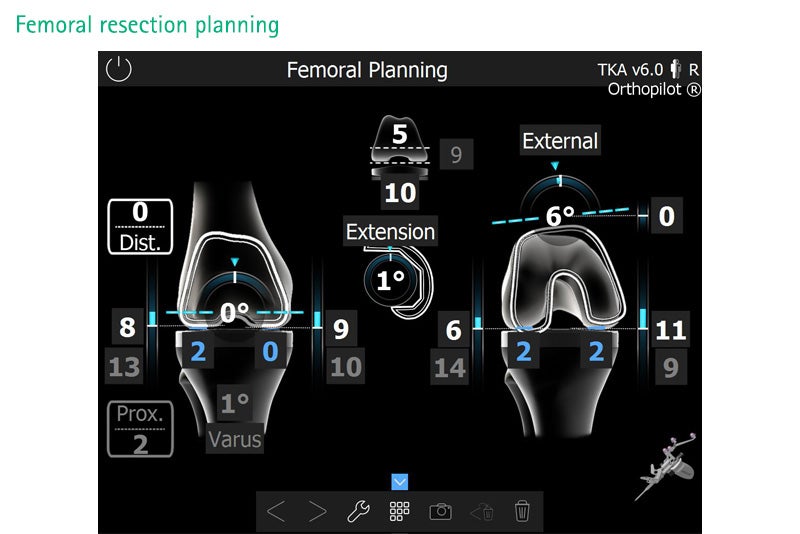
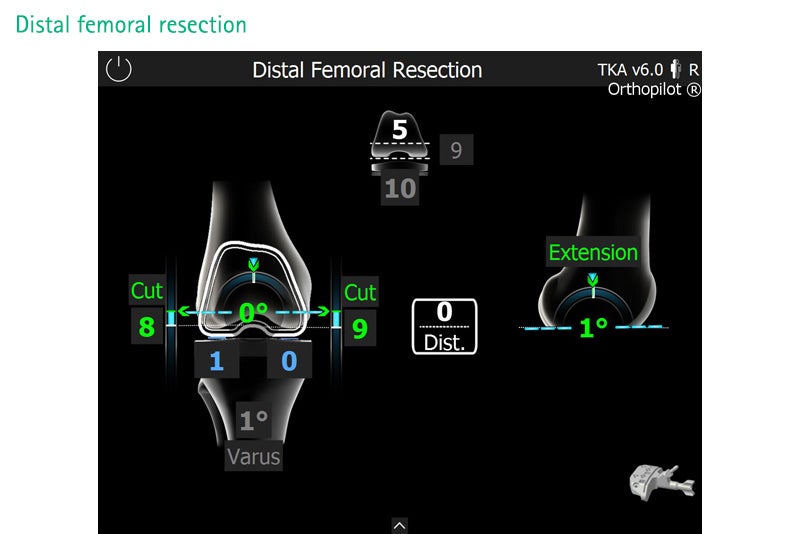
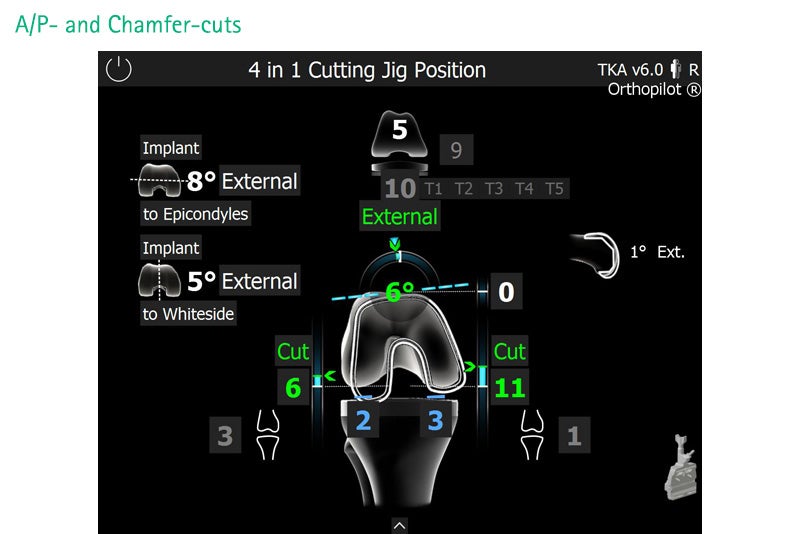
Total Knee Arthroplasty
Full control. In real time.
In surgery, precise goal achievement, performance, and real-time information are crucial to the success of the operation. OrthoPilot® Elite gives surgeons exact, continuous feedback on implant and instrument positions. So you can make the right decisions based on even more solid information.
TKA 6.0 – A new surgical experience
3 different Man-Machine-Interfaces.
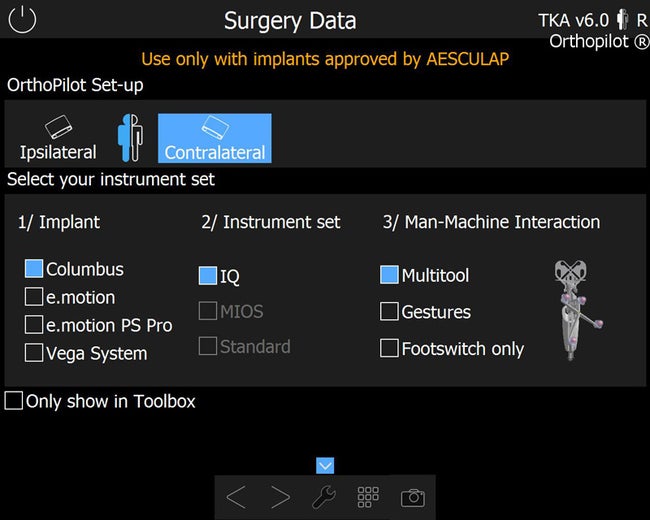
Customizable software workflow.
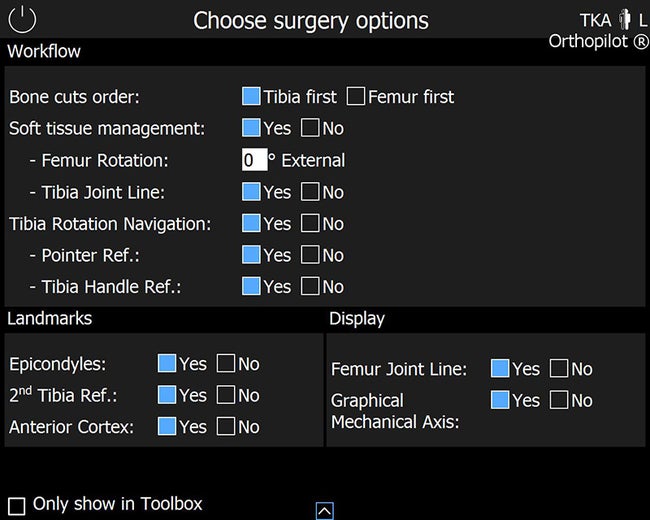
TKA 6.0 offers several surgery options to help aligning the navigation experience with your personal TKA workflow. Whether tibia rotation navigation or soft tissue management – various options can be set. Best of all: It needs to be defined once and can then be saved for upcoming surgeries so you can start collecting data immediately.
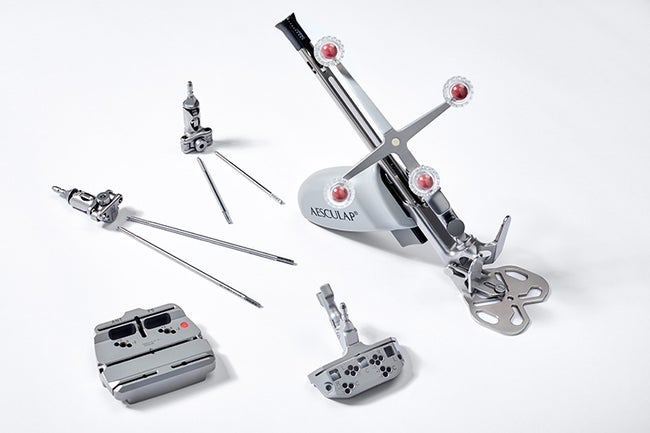
Reduced number of instruments and instrument changes.
The symbiosis of a streamlined software conceptualization and reworked navigation instrumentation simplifies the workflow, leads to a reduced number of required instruments and reduces instrument changes. Speeding up the process of data acquisition [1] and improving ease-of-use intraoperatively are two remarkable benefits of TKA 6.0.
[1] A comparison between the new TKA 6 software application and a predecessing version of TKA software application showed a significant time reduction in data acquisition of 28%. Source: Lampe et al., Cogent Engineering (2017),4:1401440.
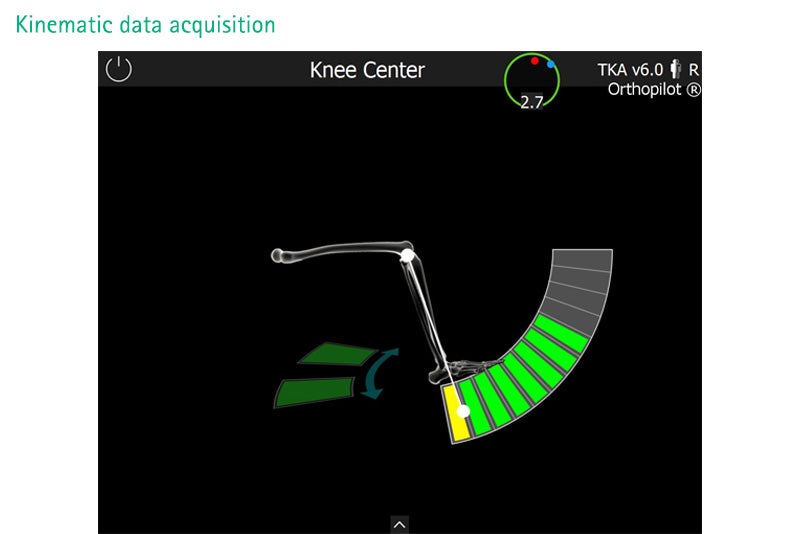
Knee kinematic module.
The new knee kinematic module shows the kinematic behaviour of the knee joint in different stages of the surgery. This optional tool allows to study the V/V-laxity of the knee along the full range of motion and depicts for every single degree of flexion the corresponding V/V-deviation. Furthermore, the contact points of the projected femoral condyles onto the tibial plane over the range of motion are displayed. Kinematic measurements can be performed at different stages in surgery, e. g. the initial situation prior to applying any corrective measures (bone cuts and/or ligament releases) vs. the post-operative situation. The knee kinematic module is especially suitable for study purposes.
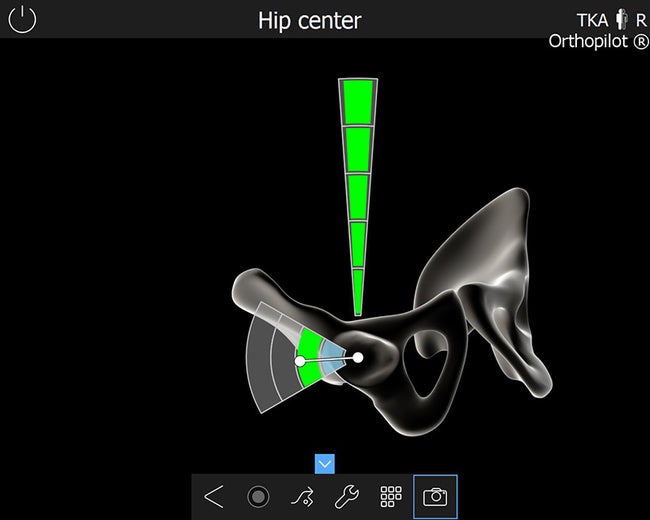
Hip center acquisition.
TKA 6.0 features a brand-new hip center acquisition movement to further simplify and accelerate the process of acquiring this essential reference for component alignment.
The robust algorithm only requires one vertical movement as well as an abduction of the femur to compute the center of the hip joint. Hip center acquisition has never been so quick and easy.
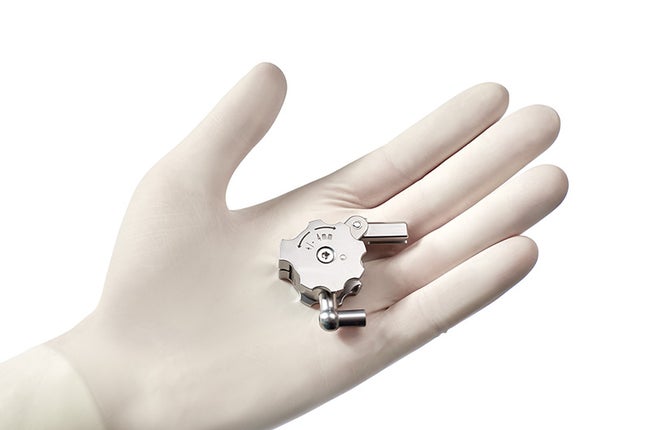
Take over control: The new Multitool.
The Multitool – a new multifunctional instrument that combines 4 instruments in 1 – serves as one possible man-machine-interface to control TKA 6.0. By combining cutting-edge technology with simple, intuitive handling the Multitool allows surgeons to operate flexible, precisely and ergonomically. Due to its‘ smart click-mechanism the footswitch becomes obsolete.
The entire control is in the palm of your hand.
Reduced invasiveness: Monocortical transmitter fixation.
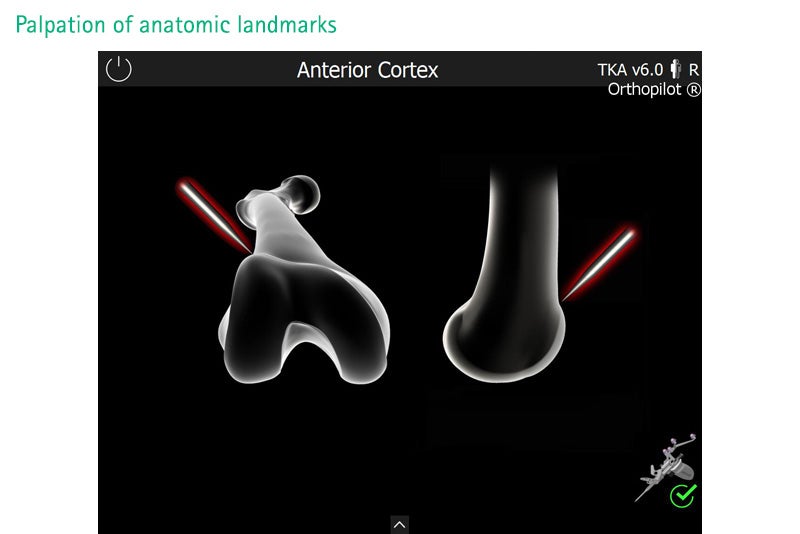
A new monocortical 2-Pin-fixation for the navigation transmitters reduces invasiveness and improves transmitter visibility. 3.2 mm pins in different lengths allow to respect the individual soft tissue situation and can be placed either through separate stab incisions or even within the incision (e. g. on the femur). Four different adapter positions and a 180° swing angle facilitate the transmitter orientation to the stereo-optical camera system and reduce efforts in camera positioning.
Precise and easy: The cut alignment instrument.
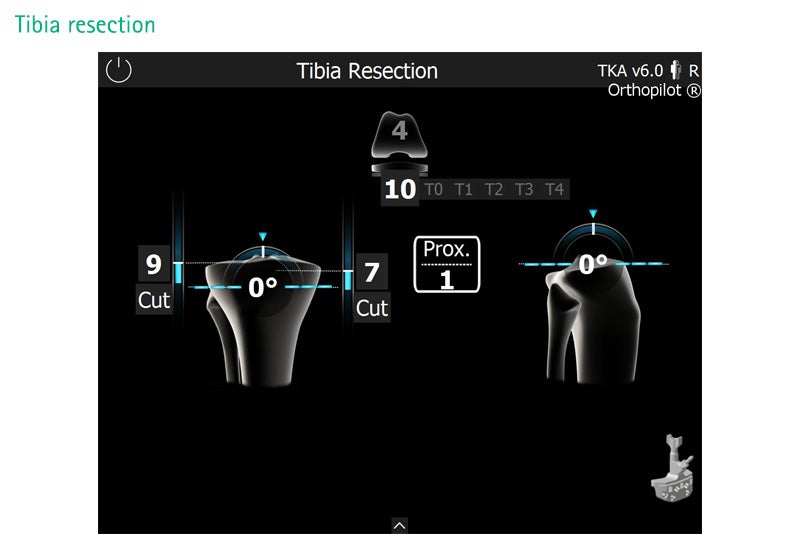
Aligning the cutting guide for the distal femur or proximal tibia resection has never been so easy. This optional instrument can be simply plugged into the corresponding cutting guide and roughly positioned in the desired cutting height. Further fine-tuning is done millimeter by millimeter and degree by degree. In doing so, all three degrees of freedom – V/V-alignment, slope and cutting height – can be taken into account step by step.
TKA 6.0 – 3D animation
-
Tibia First
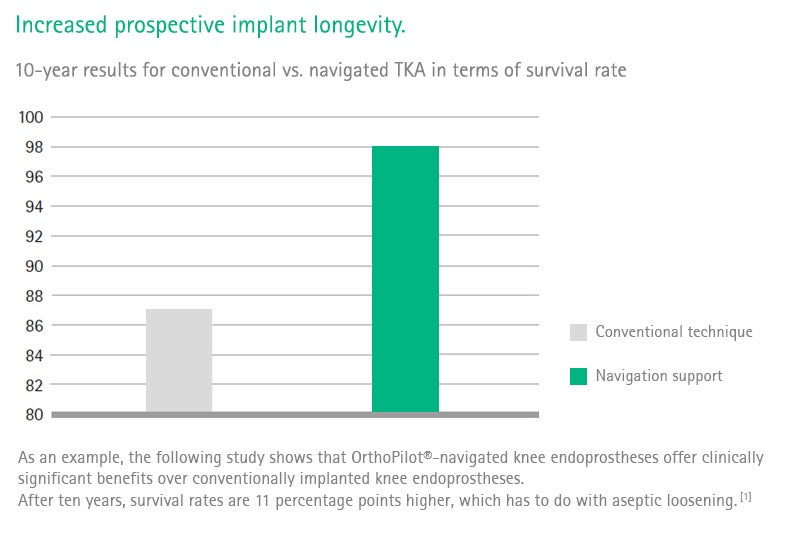
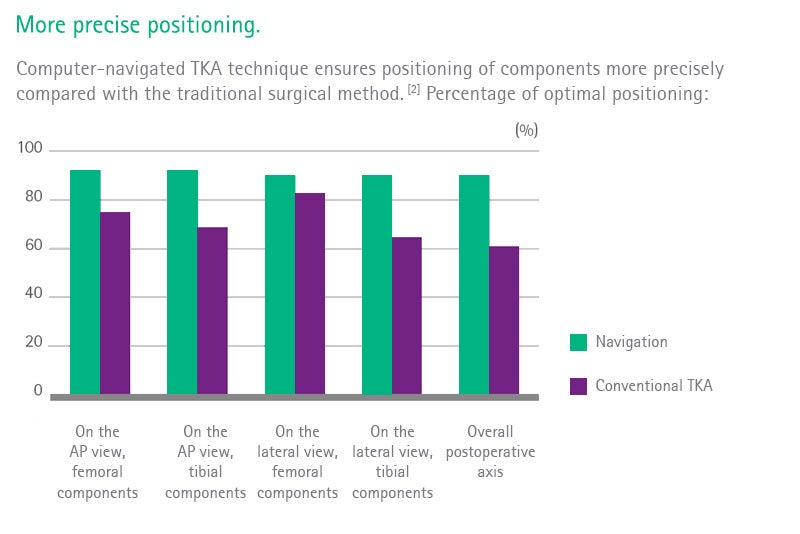
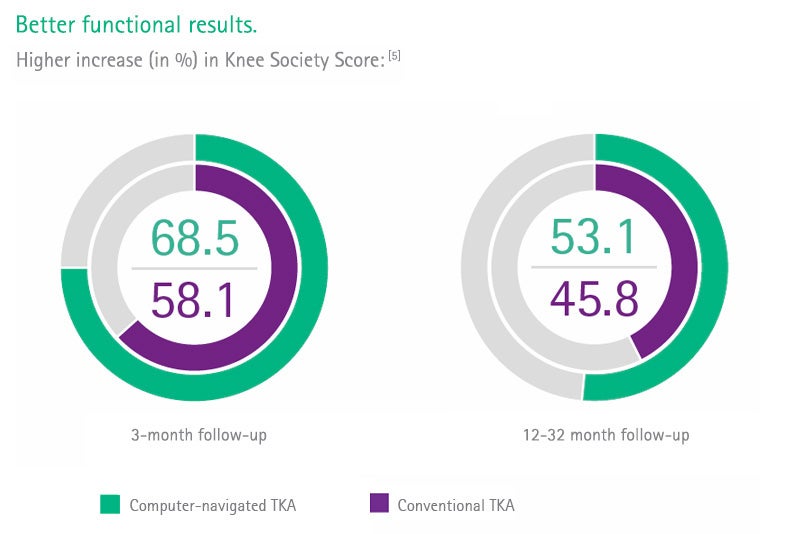
Clinical evidence
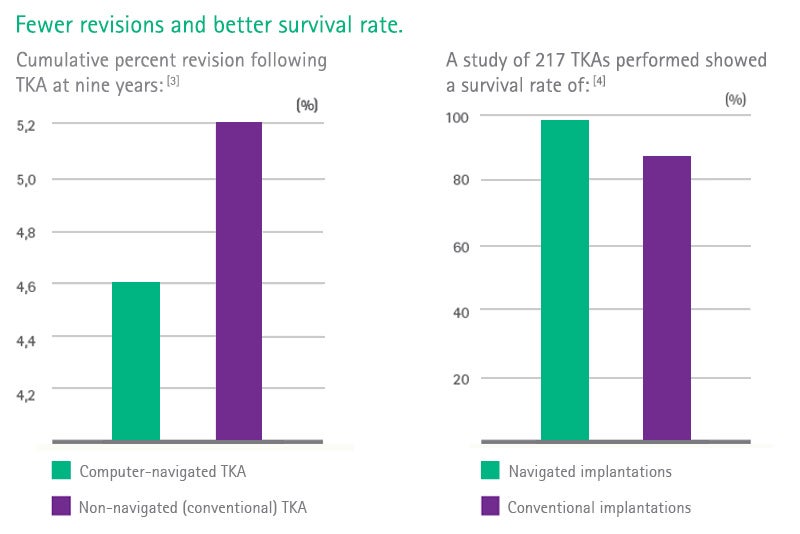
[4] Baumbach JA, Willburger R, Haaker R, Dittrich M, Kohler S. 10-Year Survival of Navigated Versus Conventional TKAs: A Retrospective Study. Orthopedics. 2016 May;39(3 Suppl):S72-6.
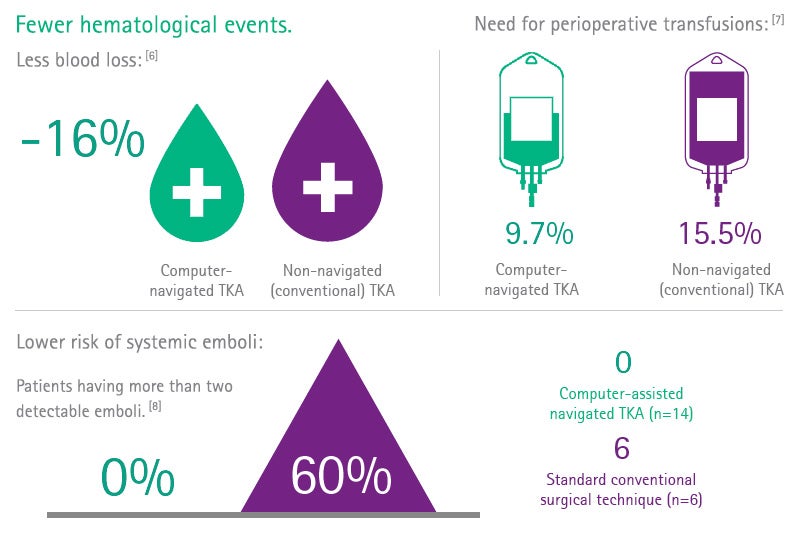
[7] Liodakis E, Antoniou J, Zukor DJ, Huk OL, Epure LM, Bergeron SG. Navigated vs Conventional Total Knee Arthroplasty: Is There a Dieffrence in the Rate of Respiratory Complications and Transfusions? J Arthroplasty. 2016 Oct;31(10):2273-7.
[8] Kalairajah Y, Cossey AJ, Verrall GM, Ludbrook G, Spriggins AJ. Are systemic emboli reduced in computer-assisted knee surgery?: A prospective, randomised, clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006 Feb;88(2):198-202.

[4] Baumbach JA, Willburger R, Haaker R, Dittrich M, Kohler S. 10-Year Survival of Navigated Versus Conventional TKAs: A Retrospective Study. Orthopedics. 2016 May;39(3 Suppl):S72-6.

[7] Liodakis E, Antoniou J, Zukor DJ, Huk OL, Epure LM, Bergeron SG. Navigated vs Conventional Total Knee Arthroplasty: Is There a Dieffrence in the Rate of Respiratory Complications and Transfusions? J Arthroplasty. 2016 Oct;31(10):2273-7.
[8] Kalairajah Y, Cossey AJ, Verrall GM, Ludbrook G, Spriggins AJ. Are systemic emboli reduced in computer-assisted knee surgery?: A prospective, randomised, clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006 Feb;88(2):198-202.