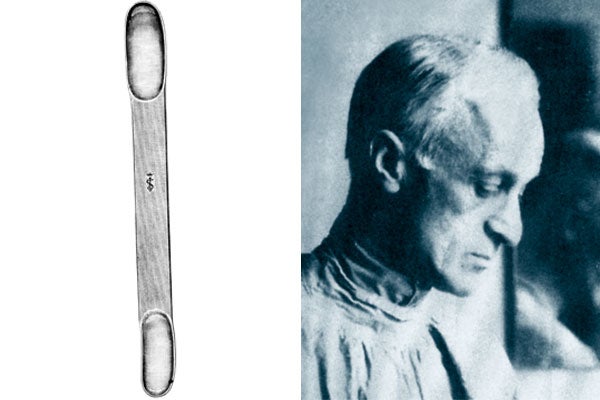
Harvey Cushing
American surgeon, New Haven, Baltimore, Boston 1869-1939, born in Cleveland/Ohio, died in New Haven/Connecticut
Cushing was the author of numerous monographs on brain surgery and developed the surgical applications of local anaesthesia. His work on the pituitary gland met with international acclaim, and his research into tumours on the auditory nerve and in the brain made him famous.
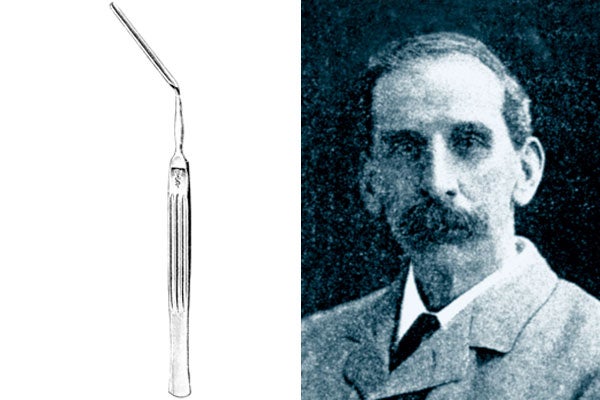
Albrecht von Graefe
German ophthalmologist, Prag, Paris, Wien, London, Berlin 1828-1870, born in Finkenheerd/Preussen, died in Berlin
Graefe's most fundamental area of activity was weak sight with no organic damage to the eye. He recognised the inflammation of the visual nerves as the cause for amblyopia and the connection between brain tumours and the so-called choked disc or papilloedema. He was also successful in strabismus surgery and iridectomy in glaucoma cases.
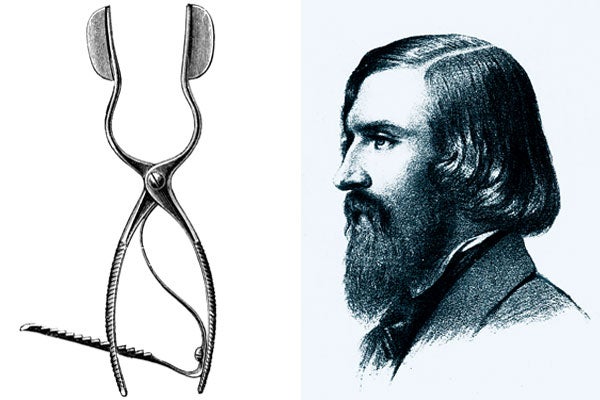
Victor Horsley
English surgeon, London 1857-1916, born in Kensington, died in Amara/Mesopotamien
As a professor of pathology and clinical medicine, Horsley was particularly concerned with the function of the thyroid gland and brain localisation. He introduced the use of thyroid extracts for the treatment of myxoedema, and performed the first operation on a tumour of the spinal cord in 1887. He also made great progress in the surgical treatment of the central nerve system.
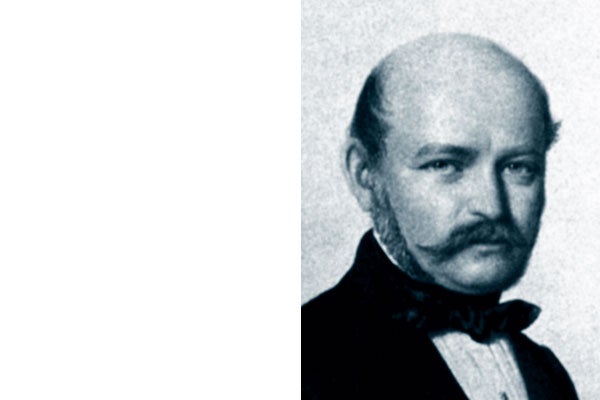
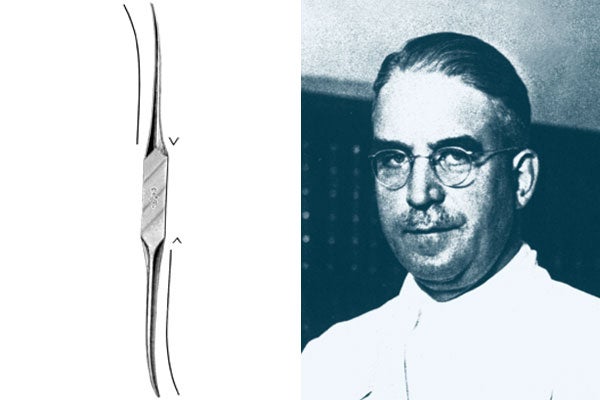
Ignaz Philipp Semmelweis
Austro-Hungarian gynaecologist and obstetrician, Vienna, Pest 1818-1865, born in Ofen/Budapest , died in Vienna
Semmelweis discovered the cause of childbed fever in an infection with putrefactive bacteria from dead bodies, these bacteria being transported from the autopsy department via the puerperium ward into the delivery rooms. Following this discovery, he successfully introduced the practice of washing the hands in a chlorinated lime solution. Thanks to Semmelweis, hygiene was introduced into operating theatres around the world.
Wilhelm Tönnis
Deutscher Neurochirurg, Stockholm, Berlin, Bochum, Köln 1898-1978, geboren in Kley/Dortmund, gestorben in Köln
Tönnis gilt in Deutschland als Pionier und Vater der Neurochirurgie. Er schreibt über 300 Arbeiten über Neurochirurgie und Hirnforschung, unter anderem über die Gefäßmissbildungen und Gefäßgeschwülste des Gehirns, die operative Behandlung des Cervikal-Vertebral-Syndroms und die Behandlung der Hypophysenadenome.