Excia® Hip Stem System
Less invasive. Modern hip replacement.
Excia® straight stems are designed for implant longevity with or without bone cement – with standard or high offset – suitable for all less invasive surgical hip approaches.
Learn more about
Cemented and Cementless Design
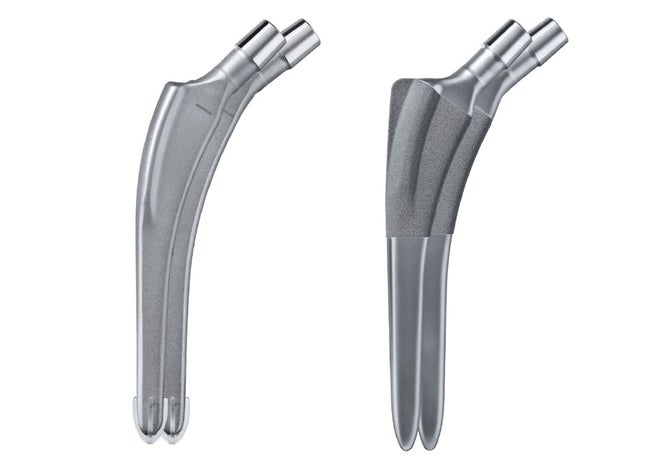
Two design options for implantation with or without bone cement with standard or high offset.
Cementless stem design from titanium alloy with distal guided fitting and proximal flanges and trochanteric wing for mechanical stability. Proximal fixation with Plasmapore® coating.
Cemented wingless stem design from Cobalt Chrome alloy preserves bone near the trochanter. The flanges ensure a good proximal fit within the cement mantle. Good stem alignment is supported by the distal centralizer.
Plasmapore® Surface
The cementless Excia® features a proximal rough Plasmapore® titanium micro-porous coating.
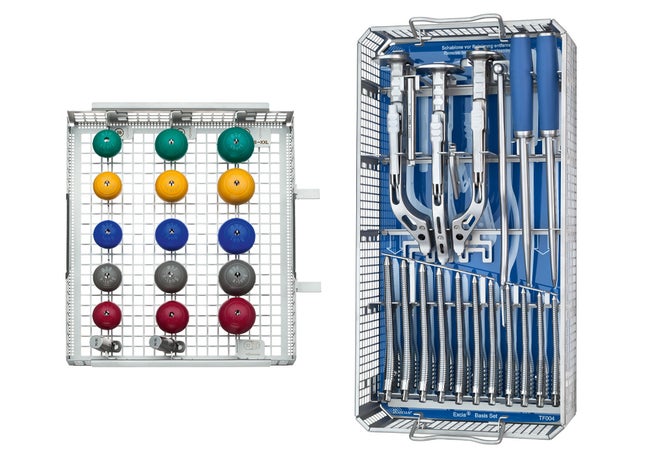
Excia® Instruments
Literature
Mainard D, Mayer J, Guignand D, Daubresse F, Porcuite JM, Galois L
Results of a bone preserving cementless straight hip stem – A prospective study with a minimum follow-up of 5 years. XXV Triennial World Congress of SICOT; 2011 September 6-9; Prague, Czech Republic.
Strecker W, Barthel G, Middeldorf S
Erste Erfahrungen und Ergebnisse mit dem Hüftprothesenschaft Excia. Frankfurter Orthopädie Symposium 2005; 159-64.
Prymka M, Vogiatzis M, Hassenpflug J
[Primary rotatory stability of robot-assisted and manually implanted hip endoprosthesis stems]. Unfallchirurg. 2004 Apr; 107(4) : 285-93. German.
Prymka M, Vogiatzis M, Hassenpflug J
[Primary rotatory stability of hip endoprostheses stems after manual and robot assisted implantation]. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb. 2004 May-Jun; 142(3) : 303-8. German.
Mayer J
[Results of a bone preserving cementless straight hip stem. A prospective study with a minimum follow-up of 5 years. A study with 237 cases.] CHU de Nancy Oct. 2010.
Biber R, Brem M, Singler K, Moellers M, Sieber C, Bail HJ
Dorsal versus transgluteal approach for hip hemiarthroplasty: an analysis of early complications in seven hundred and four consecutive cases. Int Orthop. 2012 Nov; 36(11) : 2219-23.
Mayer J, Guignand D, Poircuitte JM, Chevrollier J, Daubresse F, Galois L, Mainard D
Rèsultats à plus de 5 ans d'un implant fèmoral non cimentè prèservant le capital osseux. À propos d'une étude prospective monocentrique de 237 cas. Revue de chirurgie orthopédique et traumatologique. 2011; 97S: S248-358, Vortrag 15.
Biber R, Möllers M, Wicklein S, Singler K, Sieber C, Bail HJ
[Hemiarthroplasty for Femoral Neck Fracture in the Elderly – An Operation Suitable for Teaching?]. Zentralbl Chir. 2013 Mar 4. German.
Csotye J, Sisak K, Bardocz L, Toth K
Bilateral spontaneous displaced femoral neck fractures during pregnancy. The Journal of Trauma Injury, Infection and Critical Care. 2010 May; 68 (5): E115-6.
Urschel C, Döring M, Strecker W
Zementfreie und zementierte Excia-Hüftprothesenschäfte. Vergleich der mittelfristigen Ergebnisse. Orthopäde. 2014; 43: 815-24.