You have successfully logged out.
Not registered yet?
Neurosurgery
Challenges of surgeons
We have realized that the workflow in the OR isn't perfect yet.
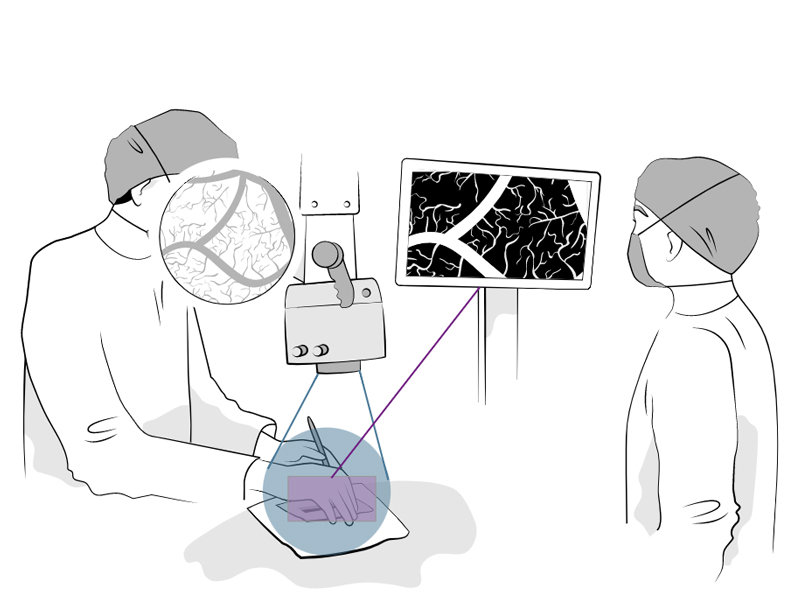
Microsurgeons faces several challenges with the current technology in terms of vision
Shallow depth of field
Surgeons spend up to 10% of surgery time on microscope adjustments and work an average of 9 times per operation under a non-focused view. [1]
Limited field of view
On average surgeons work on the edge of the view field 11 times per operation. [1] The edges of the field of view are not visible on the monitor, which is used by the team.
Illumination challenges
The visual axis and light source of optical microscopes are 3-6" apart. [2]
Inconvenient use of fluorescence imaging
Usually, either fluorescence image or white light image can be visualized, but not both at the same time. ICG fluorescence is visualized in 2D only. [3]
True pioneers deserve a better view.
But that’s not all. There are also ergonomic challenges for the surgeon.
-
4 in 0
neurosurgeons report pain after a day of surgery. [4]
-
0%
of these had musculoskeletal pain. [4]

For every inch the head moves forward, the head, neck and upper back muscles must support an additional weight of 10 POUNDS.
Potential consequences of this physical stress: [5]
True pioneers keep their heads up.
Focus on the future with pioneering technology.

Ready for a new level of vision and comfort?

A new level of vision
- Superior depth of field
- 16:9 field of view for the whole team
- Effective illumination coaxial, LED, HDR, software optimized
- 2x more information compared to conventional eypiece view
- Fluorescence mode with more information thanks to white backlight
- White light mode with fluorescence information as overlay
- More efficient workflow – improved teamwork and teaching [6]
A new level of comfort
- 3D heads-up surgery allows for an ergonomically comfortable posture (less pain, better performance) [7], [8]
- Robotic-assisted features – convenient adjustment of the camera with a robotic arm
- Facilitated workflow
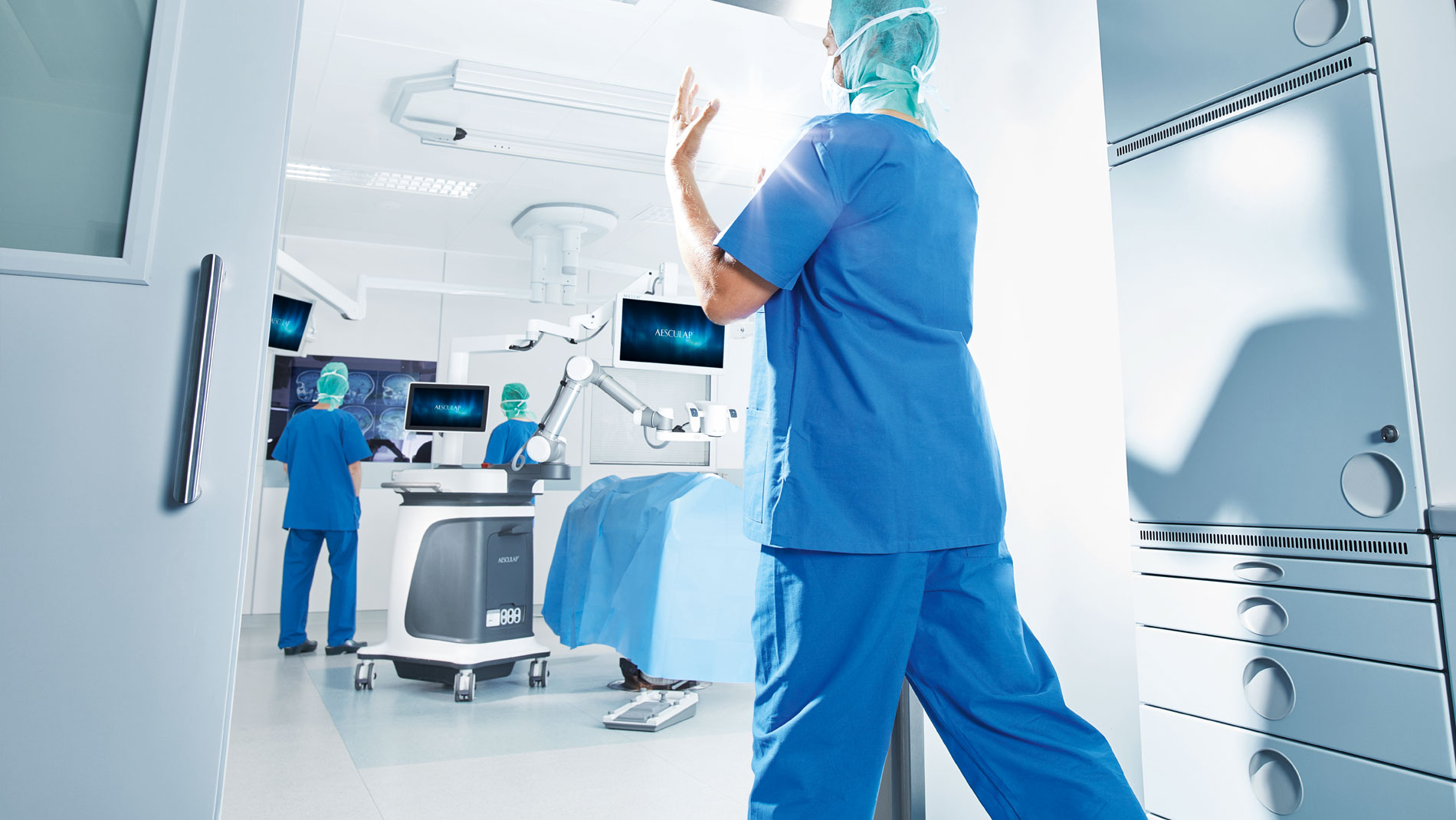
The Aesculap Aeos®
Join the future of surgical microscopy
- Fully digital
- Upgradeability with new software
- Fluorescence imaging
- Robotics
References
- Eivazi S, Afkari H, Bednarik R, Leinonen V, Tukiainen M, E Jääskeläinen J: Analysis of disruptive events and precarious situations caused by interaction with neurosurgical microscope. Acta neurochirurgica. 2015; 157:1147-1154.
- Kalani MY, Yagmurlu K, Martirosyan N, Cavalcanti D, Spetzler R: Approach selection for intrinsic brainstem pathologies. Journal of Neurosurgery. 2016; 125:1-12.
- Schutt CA, Redding B, Cao H, Michaelides E: The illumination characteristics of operative microscopes, Am J Otolaryngol. 2015; 36(3):356-60.
- Kerstin Pingel. 7 Tips For Better Ergonomics in Neurosurgery. Leica Science Lab. 2014.
- Kerstin Pingel. Ergonomically Designed Surgical Microscopes Support Performance. Leica Science Lab. 2014.
- Eivazi S, Afkari H, Bednarik R, Leinonen V, Tukiainen M, E Jääskeläinen J: Analysis of disruptive events and precarious situations caused by interaction with neurosurgical microscope. Acta neurochirurgia. 2015; 157:1147-1154.
- Kerstin Pingel. 7 Tips for Better Ergonomics in Neurosurgery. Leica Science Lab. 2014.
- Kerstin Pingel. Ergonomically Designed Surgical Microscopes Support Performance. Leica Science Lab. 2014.